16 February 2024
●
1 min read

> diving into ETFs and crypto ETFs
Imagine this: you want to invest in 10 companies but do not want to analyze the performance of these stocks deeply or individually deal with having to buy, track, or sell each. In comes an ETF. This ETF will come along claiming, “Oh, don’t worry, we are an asset that is a sum of those ten companies. Buy our ETF and only manage one thing instead of 10 separate stocks while maintaining the ability to sell at any time, just like a stock! We’ll handle the rest of the paperwork and asset optimization; all we ask for is a slice of the profits.”. But why would you go through so much trouble to invest in 10 companies when you can bet all your money on one? Short answer: diversification and risk reduction.
> ETFs in TradFi
ETFs are broadly available in 4 categories. There are index ETFs that are benchmarked to the equities market. Secondly, there are gold ETFs that are indexed to the market price of gold. Thirdly, sectoral or thematic ETFs that are benchmarked to a portfolio of stocks in a particular industry. Lastly, there are international ETFs that invest in funds abroad.
ETFs account for only a fraction of the total global financial market in equities and fixed income, ranging from 4.6%-13% of equities and 0.4%-2.8% of fixed income assets by region. You would be surprised to know that Bitcoin spot ETFs have overtaken the silver ETF market share! With these stats, you can also imagine how much potential there is in the upcoming crypto market.
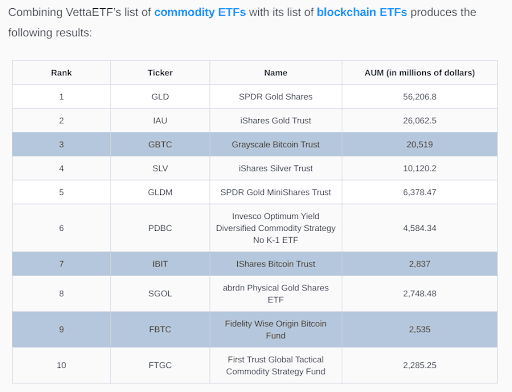
Below is a list of the top ETFs, including the new Bitcoin spot ETFs that were recently released.
> eli5: ETF vs. Mutual funds
ETFs and Mutual Funds differ in a few key ways. For one, ETFs can be actively traded on exchanges just like any other shares, while Mutual Funds can only be purchased from a fund house, even if they are listed on exchanges. Additionally, ETFs typically have no minimum lock-in period and can be bought and sold at any time by investors. On the other hand, Mutual Fund units often have a minimum lock-in period, and selling them before this period can result in a penalty. Another difference is that fund managers or professionals actively manage Mutual Funds. At the same time, ETFs are passive investments that track the performance of an index or similar set of companies/assets. One of the significant benefits of ETFs over mutual funds is their inherent tax efficiency.
> how does a Crypto ETF work?
ETFs typically track indexes by holding a selection of underlying assets. However, the methods utilized by crypto ETFs to monitor digital currency performance differ slightly. Spot ETFs directly hold the cryptocurrency, forming a portfolio that mirrors the performance of the digital assets they contain. Other crypto ETFs invest in futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell crypto at a predetermined date and price.
> spot ETFs
Spot ETFs securely hold bitcoins in a digital vault managed by registered custodians. The purpose is to mirror the price of bitcoins in the crypto market. The ETF buys crypto and stores it in a digital wallet with extra layers of security. It then issues shares corresponding to the bitcoins it holds, and these shares are available for public trading on traditional stock exchanges. Market makers ensure the ETF's liquidity and efficiency. Spot ETFs provide more opportunities for investors to speculate on the crypto without the technical challenges of managing a cryptocurrency wallet or the security concerns of safeguarding private keys.
The SEC recently approved spot bitcoin ETFs, allowing investors more accessible access to the cryptocurrency. These ETFs substantially lower the barriers to entry into the crypto market, make buying and selling bitcoins easier, and are subject to regulatory oversight to ensure transparency and protect investors. On the first day after approval, they had $4.6B of trading volume.
> futures ETFs:
Futures contracts are financial derivatives that obligate the buyer to purchase or the seller to sell an asset at a preset future date and price. In the stock market, futures contracts are traded electronically on exchanges like the CME Group. In the current market, major asset management firms are opting for spot ETFs over futures ETFs due to concerns about price trailing or, more commonly, a loss due to contango (simply put, buying high and selling low and taking that loss). People also prefer the WYSIWYG model of trading, i.e., what you see is what you get, which is what spot ETFs offer.
What is a Bitcoin ETF?
Bitcoin ETFs are ETFs that track the price of Bitcoin, allowing users to invest in Bitcoin without having to own the Bitcoin and deal with the hassle that comes with it. Major players in this area include the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (GBTC) with an AUM of over $28B, iShares Bitcoin Trust ETF (IBIT) with an AUM of $2.7B, and many other relevant players.
The bitcoin ETF marketplace has become more crowded with the recent SEC approval of 11 spot bitcoin ETFs.
Outline below are some differences between directly buying BTC and investing via ETF.

> the bottom line
Exhange-traded funds represent a cost-effective way to gain exposure to a broad basket of options. With the rise of these crypto ETFs- namely the Bitcoin-based Spot ETFs coming up, users can build a diversified portfolio, dipping their toes into the vast world of crypto.
> At aarnâ, with our âfi 100 series vault, you can participate in our equal-weighted crypto index vault, which gives a balanced exposure encompassing the top 11 crypto tokens. We might plan to release a similar product or realign the existing 100 series product to mimic ETFs! So keep a lookout for that.
about aarnâ
aarnâ is an advanced DeFi asset management platform, designed at the intersection of AI and DeFi, to help users manage their digital assets lifecycle.
