10 February 2025
●
1 min read

How Layer 2 Scaling Solutions Are Solving Ethereum’s Congestion Crisis
Ethereum is the settlement layer of the decentralized economy, securing billions in DeFi, NFTs, and on-chain applications. But its dominance comes at a cost—network congestion, gas wars, and unpredictable fees, pricing out users and throttling scalability. As Ethereum continues to onboard the next wave of adoption, its Layer 1 (L1) throughput is proving insufficient to meet the demands of high-frequency trading, yield farming, and NFT minting.
Layer 2 (L2) scaling solutions have emerged as the answer—offloading computation and execution from Ethereum’s mainnet while retaining its security. With Optimistic and ZK-Rollups at the forefront, these solutions are dramatically reducing gas fees and enabling near-instant transactions.
This article breaks down Ethereum’s congestion crisis, the mechanics of L2 scaling, and how these solutions are fueling DeFi, NFTs, and beyond.
understanding the Ethereum congestion crisis
Ethereum’s congestion crisis is an unavoidable consequence of its success. As the primary settlement layer for DeFi, NFTs, and on-chain applications, Ethereum processes thousands of transactions daily, all competing for limited block space. Every interaction—whether swapping tokens on a DEX, minting an NFT, or executing a smart contract—requires gas, and when demand spikes, so do transaction fees. Ethereum’s block size and production rate are fixed, meaning that when network activity surges, transactions pile up in the mempool, forcing users to either pay exorbitant fees for priority or endure long delays.
For DeFi users, congestion can be brutal. Gas fees during peak periods have rendered simple token swaps uneconomical, sometimes exceeding the trade value itself. Liquidations on lending platforms like Aave and Compound become inefficient, creating risk for both borrowers and lenders. NFT markets also suffer—during hyped mints, gas wars push transaction costs to unsustainable levels, pricing out smaller participants. Even basic on-chain activities, such as DAO governance voting or bridging assets, become frustratingly slow and expensive.
Ethereum’s Layer 1 alone cannot scale to meet global demand without sacrificing security or decentralization. Increasing block size or reducing block time would centralize the network, violating the blockchain trilemma. Instead, scalability must be achieved through Layer 2 solutions like rollups, which offload computation while leveraging Ethereum’s security. By bundling transactions and settling them efficiently on L1, these solutions drastically cut fees and improve throughput, ensuring Ethereum remains the dominant hub for decentralized innovation.
introducing Layer 2 solutions
Layer 2 (L2) solutions are built on top of Ethereum’s mainnet (Layer 1) to enhance scalability and reduce transaction costs while preserving the security and decentralization of the underlying blockchain. Unlike sidechains, which operate independently with their own security models, L2 solutions inherit Ethereum’s security by settling transaction data on-chain. These scaling frameworks enable users to execute transactions off-chain with finality guaranteed by Ethereum, drastically improving throughput without compromising trustlessness.
The benefits of L2 solutions are game-changing. Rollups, whether Optimistic or Zero-Knowledge (ZK), significantly lower gas fees by bundling transactions before submitting them to L1, effectively multiplying Ethereum’s transaction capacity. Faster processing speeds enable real-time trading and DeFi interactions, while reduced costs make microtransactions viable again. However, L2s come with trade-offs—Optimistic Rollups introduce a delay for fraud proof verification, while ZK-Rollups require complex cryptographic computation. Liquidity fragmentation and UX challenges also pose barriers to seamless adoption.
Despite these hurdles, L2 adoption is accelerating across DeFi. Leading protocols like Uniswap, Aave, and Curve are migrating to L2 environments to minimize gas costs and enhance efficiency. Arbitrum and Optimism have emerged as dominant Optimistic Rollup solutions, while zkSync and StarkNet push the boundaries of ZK technology. The growth of L2 transactions signals a prominent shift—Ethereum’s future is modular, and L2s are the key to scaling DeFi without sacrificing security or decentralization.
Layer 2 approaches: a closer look
Ethereum’s Layer 2 ecosystem consists of multiple scaling solutions, each designed to optimize transaction efficiency while maintaining security. These solutions differ in their execution models, trade-offs, and suitability for various use cases. Here’s a breakdown of the most prominent L2 methodologies driving Ethereum’s scalability.
State Channels
- What are they
- State channels allow two or more participants to transact off-chain, only settling the final transaction state on Ethereum.
- Transactions occur instantly between participants without requiring block confirmations.
- How they work
- Participants lock a portion of their funds in a multisig smart contract on Ethereum.
- They exchange signed messages representing transactions off-chain.
- When the channel is closed, the final state is recorded on-chain, updating the Ethereum ledger.
- Use cases
- Micropayments (e.g., streaming services, pay-per-use models)
- Gaming (instant in-game transactions)
- High-frequency transactions between fixed participants
- Limitations
- Only works for a predefined group of participants.
- Requires all participants to remain online.
- Not suitable for open DeFi environments or complex smart contracts.
Plasma
- What are they
- Plasma chains are child chains that operate independently but periodically submit cryptographic proofs (Merkle trees) to Ethereum for validation.
- Transactions occur off-chain on the Plasma chain, reducing Ethereum’s workload.
- How they work
- Users deposit funds into a Plasma smart contract on Ethereum.
- Transactions occur off-chain on the Plasma chain.
- The Plasma chain submits periodic state commitments to Ethereum for finality.
- Use cases
- High-throughput applications (e.g., gaming, enterprise solutions)
- Scenarios where delayed withdrawals are acceptable
- Limitations
- Withdrawal delays (can take days due to fraud-proof mechanisms).
- Limited support for complex smart contract interactions, making it less suited for DeFi.
- User experience challenges when moving assets between Plasma and Ethereum.
Rollups (The Leading Layer 2 Solution)
Rollups bundle multiple transactions and submit them as a single batch to Ethereum, dramatically reducing costs while retaining Ethereum’s security. There are two main types: Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups.
Optimistic Rollups
- What are they
- Assume transactions are valid by default and only execute fraud-proof mechanisms if challenged.
- Introduce a “challenge period” where incorrect transactions can be disputed.
- How they work
- Transactions are batched off-chain and posted to Ethereum as calldata.
- Validators can submit fraud proofs if they detect invalid transactions.
- If a transaction is disputed, it is re-executed on Ethereum to verify legitimacy.
- Real-World Examples
- Arbitrum – Adopted by Uniswap, GMX, and Aave.
- Optimism – Powering DeFi projects like Synthetix and Velodrome.
- Benefits
- Lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum L1.
- Increased scalability while retaining Ethereum’s security.
- Compatible with Ethereum smart contracts.
- Limitations
- Withdrawal delays (usually ~7 days due to the dispute period).
- Relies on honest actors to challenge fraudulent transactions.
ZK-Rollups
- What are they
- Use cryptographic zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-SNARKs or ZK-STARKs) to verify transactions off-chain before submitting a validity proof to Ethereum.
- Unlike Optimistic Rollups, transactions are mathematically verified, eliminating the need for a challenge period.
- How they work
- Transactions are bundled off-chain.
- A cryptographic proof (ZK-proof) is generated to verify their validity.
- This proof is submitted to Ethereum, confirming all transactions in the batch.
- Real-World Examples
- zkSync – Low-fee transactions with instant finality.
- Loopring – DeFi-focused rollup with ultra-low-cost trading.
- StarkNet – High-performance scaling with support for advanced smart contracts.
- Benefits
- Instant finality (no challenge period).
- Higher security due to cryptographic validity proofs.
- More efficient than Optimistic Rollups in the long term.
- Limitations
- Requires advanced cryptography, making implementation complex.
- Higher computational costs for proof generation.
Sidechains vs. Layer 2: understanding the difference
Many people confuse sidechains with L2 solutions, but they serve different purposes.
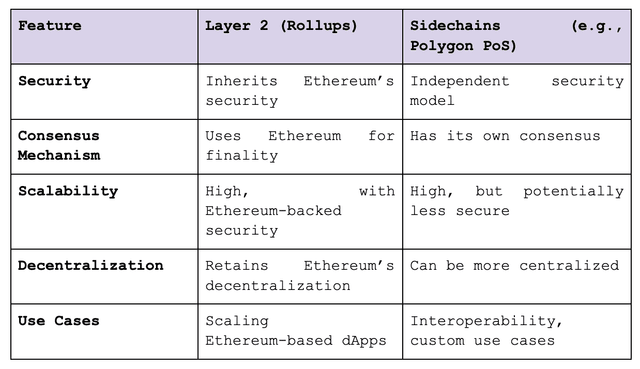
- When Sidechains Make Sense:
- Projects that prioritize speed and flexibility over Ethereum-level security.
- Games, enterprise applications, or projects requiring their own governance rules.
- When Layer 2 is Better:
- DeFi protocols, where trust and security are critical.
- Any application requiring Ethereum’s trustless architecture and composability.
Ethereum’s Layer 2 scaling landscape is rapidly evolving, with rollups emerging as the dominant solution for secure, low-cost transactions. While state channels and Plasma offer niche benefits, rollups provide the best balance of scalability, security, and decentralization. Optimistic Rollups are gaining adoption due to their Ethereum compatibility, while ZK-Rollups push the boundaries of cryptographic efficiency. As L2 adoption accelerates, Ethereum’s future is becoming modular, with Layer 2 solutions serving as the execution layer while Ethereum remains the ultimate settlement layer.
real-world examples and case studies
Ethereum’s Layer 2 ecosystem is transforming scalability, with several projects leading adoption. Arbitrum, an Optimistic Rollup, has onboarded major DeFi platforms like Uniswap and SushiSwap, reducing gas fees and easing congestion. Polygon, though a sidechain, has driven DeFi growth with Aave and QuickSwap, while expanding into Layer 2 with zkEVM for enhanced security. Loopring leverages ZK-Rollups to power its DEX, offering near-instant, low-cost trading that rivals CEXs. zkSync, built on zero-knowledge proofs, ensures secure scalability with growing DeFi integrations. These solutions have cut fees by over 90% and boosted transactions per second (TPS), proving Layer 2’s critical role in Ethereum’s future.
challenges and considerations
While Layer 2 solutions enhance Ethereum’s scalability, they come with trade-offs: > Some rely on centralized operators, raising concerns about trust and security. > Implementation is technically complex, requiring expertise to avoid inefficiencies and smart contract vulnerabilities. > Interoperability remains a challenge, as different L2 networks often lack seamless communication. > Users face onboarding difficulties, navigating asset bridging and multiple wallets, which can hinder adoption. > Regulatory uncertainty poses risks as authorities scrutinize L2 frameworks. > Economic sustainability is another concern—ensuring long-term incentives for validators and developers is critical.
Overcoming these challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of Layer 2 scaling solutions.
the road ahead for Ethereum and Layer 2
Ethereum’s future is anchored in Layer 2 scaling, with Optimistic and ZK-Rollups leading the charge in offloading execution while inheriting Ethereum’s security guarantees. As adoption intensifies, these rollups will continue optimizing finality and slashing gas fees, making transactions seamless and cost-efficient. With proto-danksharding and full EIP-4844 implementation on the roadmap, Ethereum’s throughput is set to skyrocket beyond 100,000 TPS, reinforcing Layer 2 as the de facto execution layer.
Interoperability upgrades will enable cross-rollup liquidity, eliminating fragmented ecosystems, while native account abstraction will streamline UX, making self-custody and gasless transactions mainstream. With Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) complete, sustainability remains a core focus, reducing the network’s energy footprint while maintaining cryptographic integrity.
As Layer 2 ecosystems mature, Ethereum is evolving into a modular blockchain powerhouse, where settlement, execution, and scalability work in perfect synergy. The future of DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 isn’t just multi-chain—it’s Ethereum-first, with L2s leading the way.
about aarnâ
aarnâ is an advanced DeFi asset management platform, designed at the intersection of AI and DeFi, to help users manage their digital assets lifecycle.
